Ingrown Toenails
Ingrown Toenails
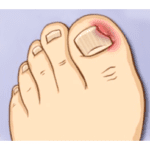 An ingrown toenail is a result of a nail growing into the skin that surrounds it. The big toe is the most common location but it may occur in any digit. At ETFA, ingrown toes nails are very common. Too often these ingrown toenails are not cared for quickly enough and infection has typically set in when they arrive in our office. Ingrown toenails may cause pain at the tip of the toe or all the way down to the base of the toe and are usually more painful when walking and when wearing shoes.
An ingrown toenail is a result of a nail growing into the skin that surrounds it. The big toe is the most common location but it may occur in any digit. At ETFA, ingrown toes nails are very common. Too often these ingrown toenails are not cared for quickly enough and infection has typically set in when they arrive in our office. Ingrown toenails may cause pain at the tip of the toe or all the way down to the base of the toe and are usually more painful when walking and when wearing shoes.
A red, swollen, painful nail margin is very common with infection of the ingrown toenail and often times there will also be bleeding and pus. Parents should be aware that children are often times slow to discuss this problem and if they get any hint that there might be a problem such as altered gait, sock stains or a grimace they should inspect the child’s toes immediately. We perform many toenail procedures and take many steps to make this as comfortable and pain-free as possible.
Ingrown toenails have many potential causes. Some of the most common are:
- Improperly fitting shoes.
- Trauma to the toe.
- Thickened toenails due to fungus or repeated trauma.
- Improper trimming of toenails.
Treatment of an ingrown toenail typically involves addressing any bacterial infection in the skin first. Surface infection may often respond to proper foot soaks or antibiotic creams and oral antibiotics may also be used depending on the severity of the infection. A removal of the offending toenail is generally required and is often performed under local anesthesia. At this point, the toenail edge may be removed and allowed to re-grow or it may be removed permanently, this is called a matrixectomy. Please call ETFA if you are suffering with an ingrown toenail and we will help you return to an active pain free lifestyle as quickly as possible.
PLEASE NOTE:
The information contained in this article is not intended to provide advice for individual problems, nor to substitute for professional advice or care from a physician. For answers to specific questions concerning your personal circumstances, you should consult your physician directly.
